
Video surveillance has become a critical part of how businesses, institutions, and even homes protect their spaces. From preventing theft to monitoring daily operations, the effectiveness of any surveillance setup depends heavily on the recording system behind it. That’s where the choice between a network video recorder and a DVR becomes important.
While both systems are designed to capture and store video footage, they work in very different ways. The type of recorder you choose affects video quality, scalability, remote access, and long-term costs. Many organizations upgrading their security often struggle with understanding whether modern NVR surveillance or traditional DVR setups better match their needs.
As technology has shifted toward IP cameras and cloud-connected systems, the debate around NVR vs DVR has become more relevant than ever. In this guide, we’ll break down the key differences in simple terms, helping you make an informed decision based on performance, flexibility, and future readiness.
You can Listen to this Blog here.
What Is a Network Video Recorder (NVR)?
A network video recorder is a modern surveillance device designed to record video footage from IP (Internet Protocol) cameras over a network. Unlike older systems, an NVR does not rely on analog signals. Instead, cameras capture digital video and send it directly to the recorder through an Ethernet network.
So, what is NVR in simple terms? Think of it as the brain of a smart surveillance setup. The cameras do most of the heavy lifting—capturing and encoding high-quality video—while the NVR stores, manages, and organizes that footage in one central place.
An NVR surveillance system typically includes IP cameras, network switches, storage drives, and software for monitoring and playback. Because everything runs on a network, users can easily access live feeds or recorded video remotely through web dashboards or mobile apps. This flexibility makes NVR systems especially popular with businesses, multi-location setups, and organizations planning to scale.
Another key advantage of an NVR is image quality. Since data is captured digitally from the start, a network video recorder supports higher resolutions, clearer images, and advanced features like motion detection and analytics. This is one of the main reasons NVR technology has become the foundation of modern surveillance systems.
What Is a DVR and How Does It Work?
A DVR, or Digital Video Recorder, is a traditional surveillance recording system commonly used with analog cameras. Unlike a network video recorder, a DVR processes video footage after it has been recorded. Cameras send raw analog signals to the DVR using coaxial cables, and the recorder then converts those signals into digital video for storage.
In a DVR-based setup, the recorder plays a much bigger role. Since analog cameras don’t encode video themselves, the DVR handles compression, processing, and storage. This approach has been around for years and is still found in many older or budget-friendly surveillance installations.
DVR systems are often chosen for smaller environments where advanced features aren’t a priority. They are relatively straightforward to install and typically cost less upfront. However, limitations in resolution, flexibility, and remote access make DVRs less adaptable to modern security needs.
While DVR technology still serves a purpose, especially in legacy systems, it lacks the scalability and performance expected from today’s surveillance solutions. This difference becomes even clearer when comparing DVR setups with modern NVR surveillance systems designed for digital-first environments.
Also Read,
Video Surveillance Systems for Business: What You Need to Know
NVR vs DVR: Core Technology Differences
The biggest difference between an NVR and a DVR lies in how video data is captured, processed, and transmitted. Understanding these technical differences makes it much easier to choose the right system for your surveillance needs.
A network video recorder works with IP cameras that capture and encode video digitally at the camera level. This video is then sent over a network using Ethernet cables or wireless connections. Because the footage is already digital, the NVR focuses mainly on storage, management, and playback.
In contrast, DVR systems rely on analog cameras that transmit raw video signals through coaxial cables. The DVR itself is responsible for converting this footage into digital format before storing it. This extra step limits flexibility and affects video quality.
Another major distinction is camera compatibility. NVR systems are designed for modern IP cameras, which offer advanced features like remote access, motion analytics, and higher resolutions. DVRs are tied to analog cameras, making upgrades more restrictive.
When it comes to cabling, NVR surveillance systems often use a single Ethernet cable for power and data, simplifying installation. DVR setups require separate power and video cables, which can increase complexity. These core technology differences explain why many businesses now prefer network-based recording over traditional DVR solutions.
Video Quality and Performance Comparison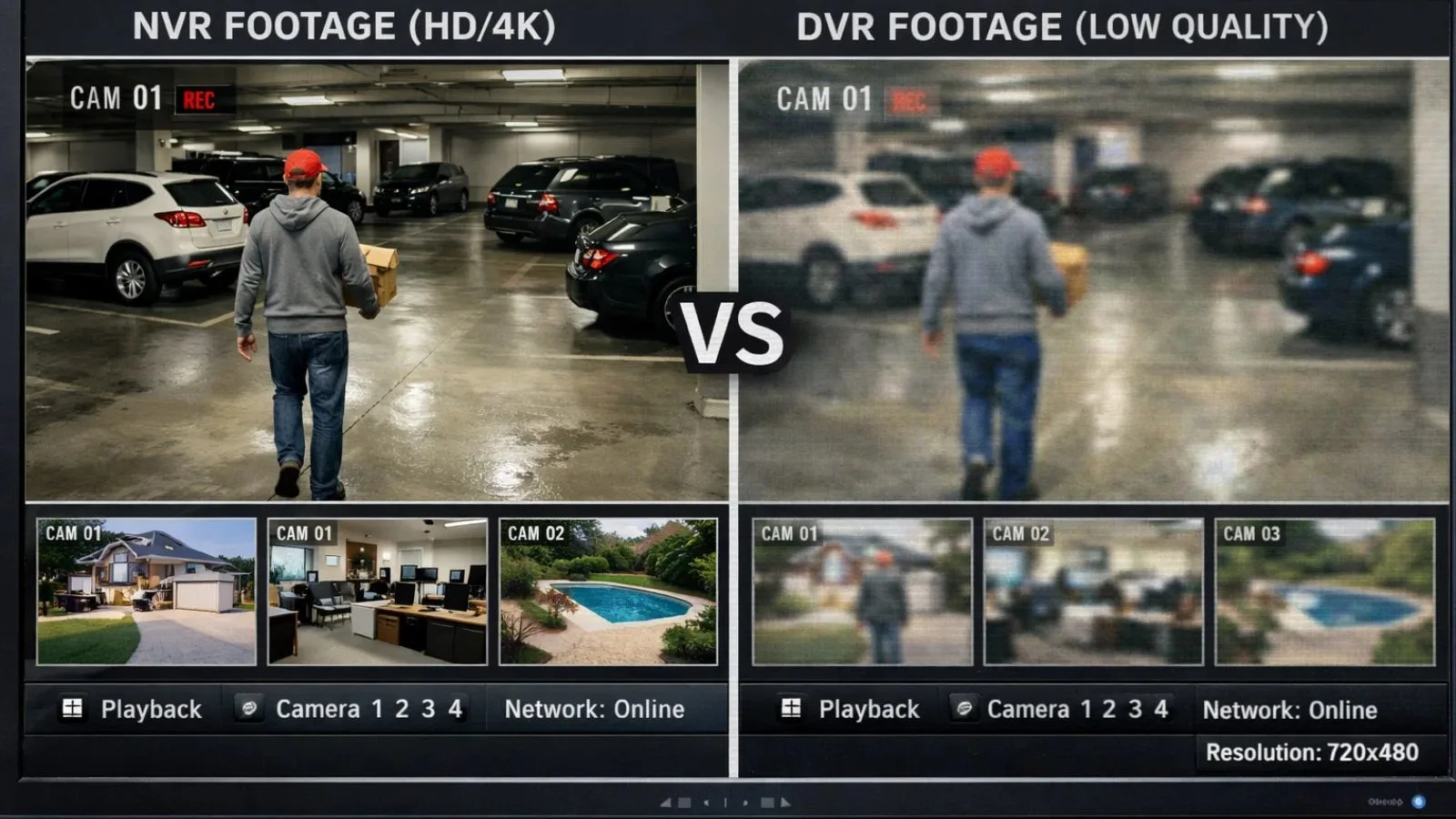
Video quality is one of the most noticeable differences when comparing an NVR and a DVR. A network video recorder supports high-resolution digital footage because IP cameras capture and transmit video in digital form from the start. This results in sharper images, better color accuracy, and clearer details, which are essential for identifying faces, license plates, or suspicious activity.
Most NVR surveillance systems support HD, 4K, and even higher resolutions, along with better frame rates and modern compression standards. Since processing happens at the camera level, performance remains consistent even as systems scale.
DVR systems, on the other hand, are limited by analog camera technology. While newer DVRs may offer improved resolution compared to older models, they still cannot match the clarity and flexibility of network-based recording. Video quality often degrades over long cable distances, and image enhancement options are limited.
Performance also extends to reliability. NVR systems handle multiple video streams more efficiently and are better suited for environments requiring continuous monitoring. For businesses and organizations that depend on accurate footage, the performance advantage of a network video recorder becomes a decisive factor.
Installation, Scalability, and Flexibility
Installation and future expansion are key considerations when choosing between an NVR and a DVR. A network video recorder is designed with flexibility in mind, making it easier to install and scale as surveillance needs grow.
NVR surveillance systems typically use Ethernet cables to transmit both power and data through Power over Ethernet (PoE). This reduces wiring complexity and allows cameras to be placed wherever there is network access. Adding new cameras is usually as simple as connecting them to the network and configuring them through software.
DVR systems are more rigid. They rely on coaxial cables for video and separate power connections, which can limit camera placement and make expansions more labor-intensive. Adding cameras often requires additional cabling and hardware upgrades.
Scalability is another major advantage of NVR systems. Whether you’re monitoring one location or multiple sites, a network video recorder can grow with your setup. Cloud connectivity and software integrations further enhance flexibility, allowing users to adapt their surveillance strategy over time. For businesses planning long-term security, NVR solutions provide a much more future-ready foundation.
Storage, Access, and Remote Monitoring
How video footage is stored and accessed plays a major role in day-to-day surveillance operations. A network video recorder offers more flexible and secure storage options compared to traditional DVR systems, making it better suited for modern monitoring needs.
NVR surveillance systems typically support a combination of local storage, network-attached storage, and cloud-based backups. This allows users to scale storage capacity easily and maintain redundancy for critical footage. Advanced encryption and user access controls also help protect sensitive video data.
Remote access is another area where NVR systems stand out. Because footage is managed over a network, users can view live feeds, search recordings, and receive alerts from anywhere using a web browser or mobile app. This level of accessibility is essential for businesses managing multiple locations or remote teams.
DVR systems usually rely on local storage with limited remote functionality. While some DVRs offer basic online access, they often lack the speed, reliability, and security of network-based solutions. For organizations that need real-time visibility and centralized control, the advantages of a network video recorder become clear.
Cost Considerations: NVR vs DVR
Cost is often one of the first factors people evaluate when choosing a surveillance system. At first glance, DVR setups may seem more affordable, but the long-term value tells a different story when compared with a network video recorder.
DVR systems generally have lower upfront costs. Analog cameras and DVR hardware are typically cheaper, making them appealing for small installations or short-term use. However, these systems can become expensive over time due to limited upgrade options, additional cabling, and frequent hardware replacements.
NVR surveillance systems may require a higher initial investment, especially for IP cameras and networking equipment. That said, the return on investment is often better. Higher video quality, easier scalability, and reduced maintenance costs make NVR systems more cost-effective in the long run.
When factoring in future expansion, remote monitoring, and software upgrades, a network video recorder delivers more value for growing businesses. Instead of replacing entire systems, users can simply add cameras or storage as needed, keeping overall costs under control.
Why Choose VideoraIQ?
Choosing VideoraIQ means moving beyond passive video recording to intelligent visual awareness. While a network video recorder securely stores high-quality footage, VideoraIQ analyzes that data in real time to surface actionable insights. It enables faster response, stronger compliance, and smarter decisions by turning surveillance into a proactive system. Together with NVR infrastructure, VideoraIQ transforms security from simple monitoring into a strategic layer of protection and business intelligence.
Key Features of VideoraIQ
- AI-Powered Video Analytics: VideoraIQ analyzes live and recorded footage from NVR surveillance systems to detect unusual behavior, motion patterns, and predefined events, helping teams respond faster to potential risks.
- Real-Time Alerts & Notifications: Get instant alerts when specific activities occur, allowing security teams and business operators to take immediate action instead of reviewing footage after an incident.
- Centralized Monitoring Dashboard: VideoraIQ provides a unified dashboard to monitor multiple cameras, locations, and NVR systems from one place, making it ideal for businesses with distributed operations.
- Scalable & NVR-Compatible: Designed to work with modern network video recorder environments, VideoraIQ scales easily as new IP cameras or locations are added—without disrupting existing infrastructure.
Operational Insights Beyond Security: In addition to safety, VideoraIQ helps businesses analyze footfall, movement trends, and operational efficiency using data already captured by NVR surveillance systems.
Also Read,
Why Every Business Needs Live Video Monitoring?
Conclusion:
Choosing between an NVR and a DVR comes down to understanding your current needs and future goals. While DVR systems may still serve basic surveillance requirements, they fall short when it comes to scalability, image quality, and remote accessibility. In contrast, a network video recorder offers a modern, flexible foundation that supports high-resolution video, advanced analytics, and seamless expansion.
As surveillance technology continues to evolve, NVR surveillance systems stand out as the more future-ready option. They integrate easily with intelligent platforms, support centralized monitoring, and deliver long-term value for businesses of all sizes. For organizations looking to move beyond basic recording, pairing a network video recorder with solutions like VideoraIQ can transform security into a proactive, insight-driven operation.
Ultimately, the right choice depends on how much control, visibility, and growth you expect from your surveillance system. For most modern environments, NVR systems provide the clarity, flexibility, and performance needed to stay secure.
FAQ’s
1.How long can an NVR store video footage?
Storage duration depends on camera resolution, frame rate, and hard drive capacity. Many NVR systems allow easy expansion with additional storage drives or cloud backup options.
2.Do NVR systems require the internet to function?
No, NVRs can record video locally without the internet. However, internet access is needed for remote monitoring, alerts, and cloud storage features.
3.Can I upgrade from a DVR to an NVR system?
Yes. Upgrading usually requires replacing analog cameras with IP cameras and connecting them to a network video recorder. This allows you to benefit from higher resolution, scalability, and remote access.



